Create Cluster
A Kubernetes cluster is a set of nodes (masters and workers) that run containerized applications. By creating a cluster in Vietnix Cloud, you can manage, scale, and deploy your workloads efficiently.
Requirements
- You have an SSH key added to your Vietnix Cloud account.
- You have a Network created in your Vietnix Cloud account
- Your project has available resources to create nodes (CPU, RAM, and disk).
- Familiarity with Vietnix Cloud Dashboard and Cloud flavors (node sizes).
- Recommended cluster configuration (to avoid errors):
- Master: 3 nodes,
largeflavor, 40 GB boot volume, 30 GB container volume - Worker: 1–2 nodes,
mediumflavor, 20–50 GB container volume - Kubernetes version: v1.31.2
- Auto scaling: Enabled
- Master: 3 nodes,
- A personal computer with kubectl installed or accessible. Install kubectl
Create Cluster Kubernetes
-
Login to Vietnix Cloud Dashboard
-
Navigate to Kubernetes
-
Click Create Kubernetes cluster
-
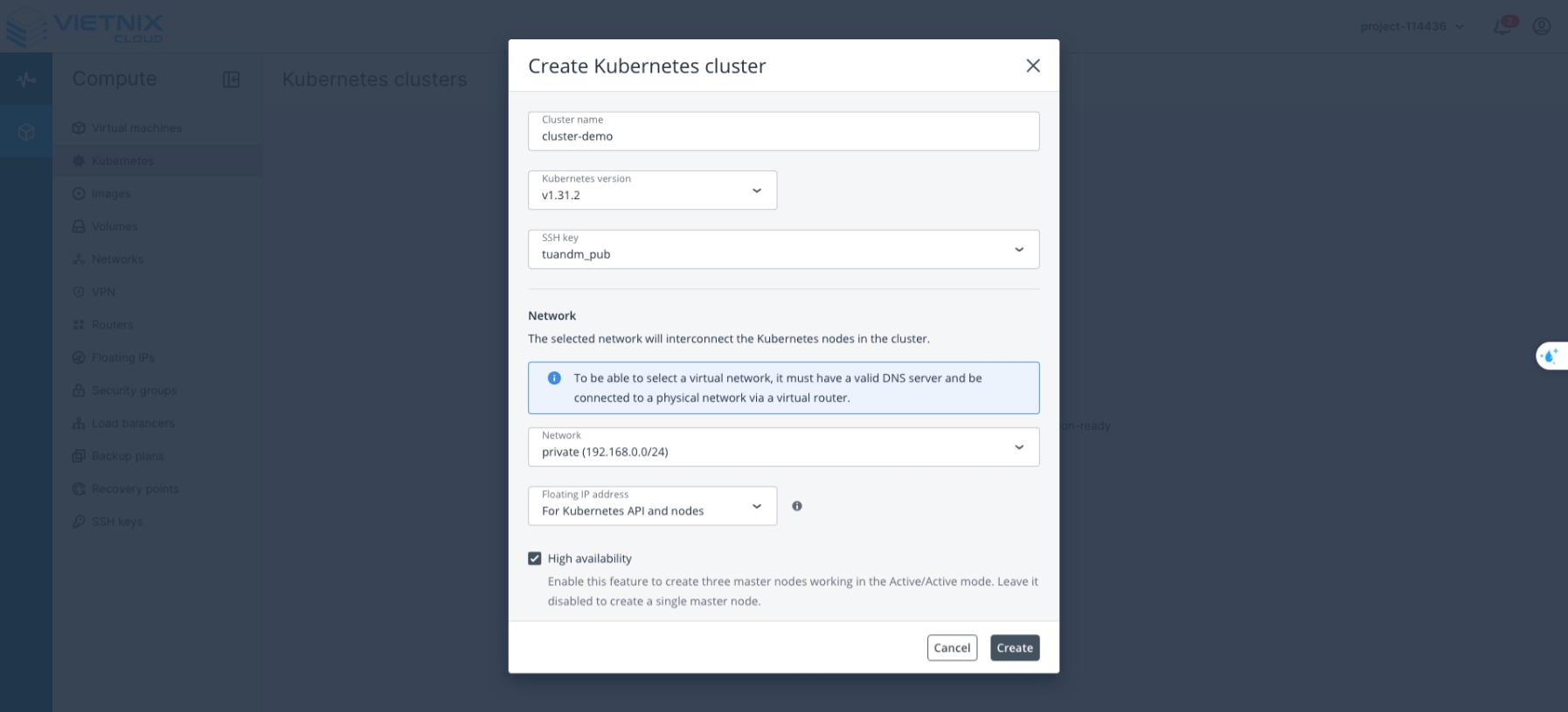
Enter the following information:
- Cluster Name: The name of your cluster
- Kubernetes Version: The Kubernetes version to use
- SSH Key: The public key used to access all nodes
- Network: The network layer that the cluster nodes (master and worker) will use
- Floating IP Address:
- For Kubernetes API and Nodes: The Floating IP will be assigned to both the API server and all cluster nodes. This allows direct access from the internet to every node (useful for SSH, monitoring, or troubleshooting individual nodes).
- For Kubernetes API: The Floating IP is assigned to the API server only. Worker nodes will have only private IPs, which improves security and reduces public IP usage. To access worker nodes via SSH, you need to go through the master node (bastion) or use a VPN.
- High Availability: When enabled, the cluster will have 3 master nodes instead of 1
- Master Node:
- Flavor: The configuration of each master node
- Container Volume: The storage size for each master and worker node (default: 20 GB)
- Default Worker Group: The flavor assigned to each worker node in the cluster
- Autoscaling: Enables automatic horizontal scaling of worker nodes. If worker nodes become overloaded, new nodes will be added automatically to balance the load.
- Number of Nodes: The total number of worker nodes in the cluster
- Click Create to deploy the Cluster Kubernetes.
-
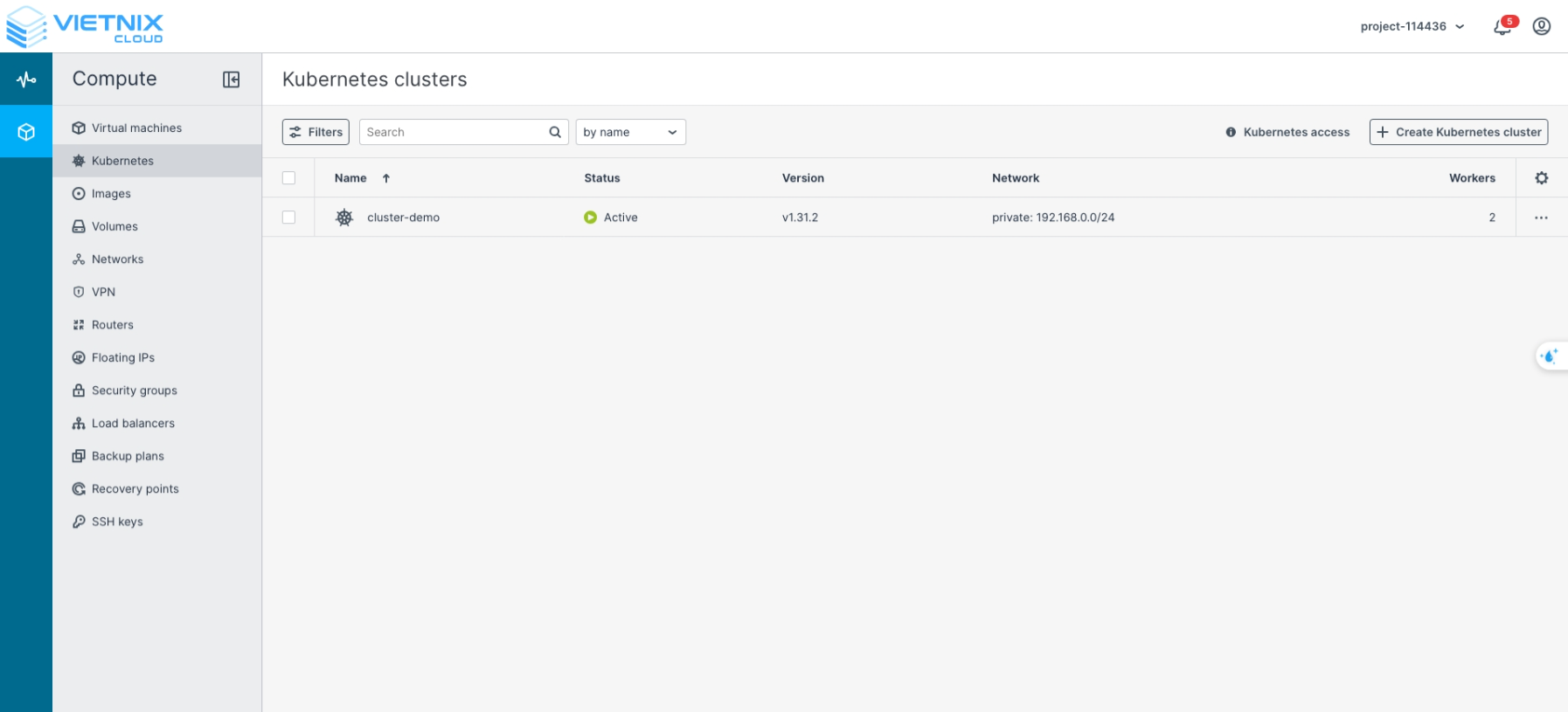
After successful creation
Best Practices
Here are recommended cluster models and operational guidelines when creating Kubernetes clusters in Vietnix Cloud.
Recommended cluster models
Development / Test
- Purpose: quick prototyping, testing, and cost efficiency.
- Suggested configuration:
- Masters: 1 master node (or 3 for HA testing).
- Workers: 1–2
mediumflavor nodes. - Container volume: 20–40 GB per node.
- Floating IP: For Kubernetes API only to reduce public exposure.
- Notes: use resource quotas, prefer lightweight workloads, and align the Kubernetes version with staging/production where possible.
Production
- Purpose: stable, highly available workloads.
- Suggested configuration:
- Masters: 3 master nodes (High Availability enabled) using
largeflavor. - Workers: 2 or more worker nodes; consider multiple worker groups for different workload types.
- Container volume: 30–100 GB or more depending on workload requirements.
- Floating IP: For Kubernetes API only for better security.
- Masters: 3 master nodes (High Availability enabled) using
- Notes: enable autoscaling, use persistent volumes for stateful workloads, apply network policies, and monitor resources continuously.
Operational recommendations
- Infrastructure as Code: define cluster configuration with Terraform/Ansible for repeatability.
- RBAC and least privilege: configure Role-Based Access Control and limit cluster-admin access.
- Network policies: restrict traffic between pods and namespaces.
- Resource requests & limits: always define CPU and memory requests/limits for workloads.
- Monitoring & logging: deploy Prometheus, Grafana, and centralized logging.
- Backups: schedule regular backups of etcd and persistent volumes.
- Security: enforce container image scanning and use admission controllers.
- Upgrade strategy: test upgrades in staging and use rolling updates in production.
- Access control: avoid exposing worker nodes; use bastion hosts or VPN when SSH is needed.