I confuse with Router and FloatingIP
You just registered an account in Vietnix Cloud, have a plan to build a huge system with many VMs, clusters, databases,... But then, you get stuck at the very beginning because you don't understand what is Router and FloatingIP, and what do they really do in Vietnix Cloud?
What is Router?
A Router in Vietnix Cloud is a virtual network device that connects different networks together. It allows communication between instances in different networks and provides access to external networks, such as the internet.
What is FloatingIP?
A Floating IP in Vietnix Cloud is a public IP address that can be dynamically assigned to any instance within a project. It allows you to expose your instances to the internet and provides a way to manage the IP addresses of your instances more flexibly. Floating IPs can be remapped to different instances as needed, making it easier to manage failover and load balancing scenarios.
What do they really do in Vietnix Cloud?
When you create a virtual machine (VM) in Vietnix Cloud, it is typically assigned a private IP address from the internal network. At this point, the VM cannot send or receive any traffic from the Internet, nor talk to VMs that live in other networks inside the cloud. It is isolated within its own internal (private) Layer-2 network.
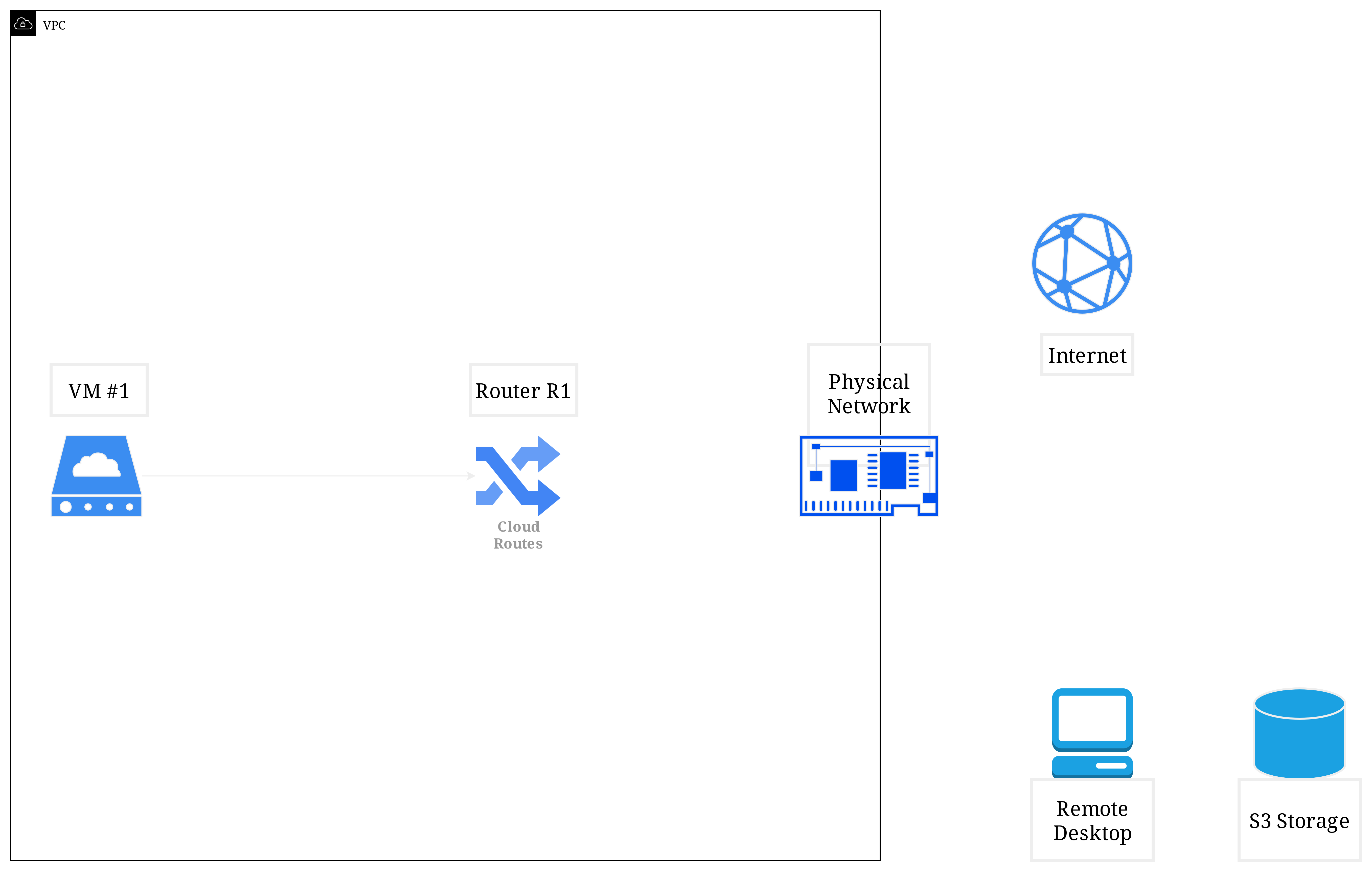
❓So how can you make your VM accessible from the Internet or other networks?
This is where Routers and Floating IPs come into play!
When you have an account in Vietnix Cloud, you are provided with a default Physical Network. A Router will create a port connecting your VM's internal network to this Physical Network, allowing it to send and receive traffic from the Internet. It also can provide an internal routing function, allowing VMs in different internal networks to communicate with each other.
Now your VM can send and receive traffic from the Internet, you can use built-in console tool in Vietnix Cloud Dashboard to access your VM and do things such as: surf the web, download files,... (If your VM is Windows system) or execute commands like: ping, tracert, curl, update, install,... (If your VM is Linux system).
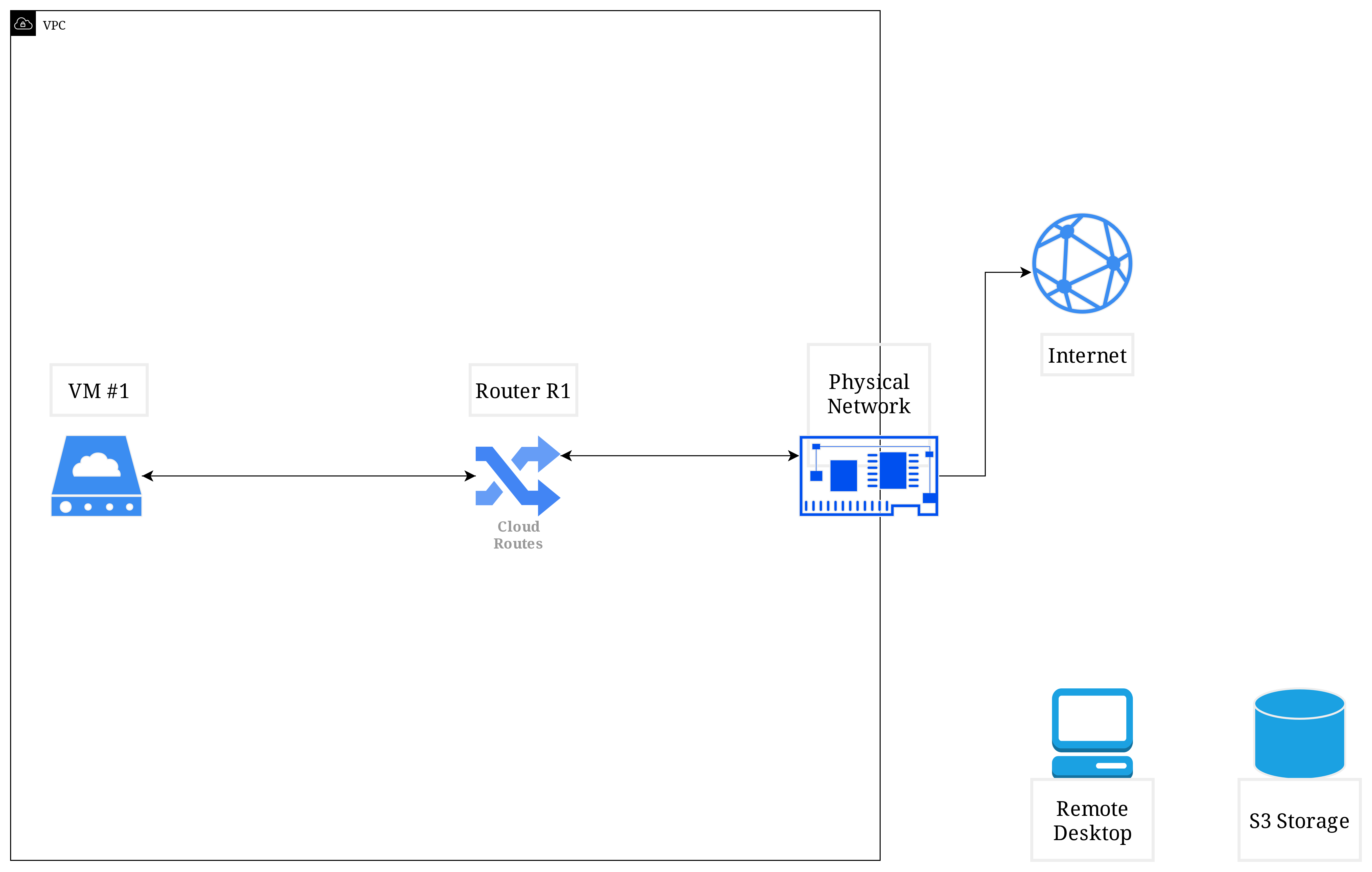
But! How can you access to your VM with ssh or rdp from your local computer? Or you have additional services that need to connect to your VM from the Internet? You need a Floating IP for that!
The Physical Network also has a pool of public IP addresses, called Floating IPs. You can allocate a Floating IP from this pool and associate it with your VM. This Floating IP will be mapped to the private IP address of your VM via the port created by the Router. Now you can access your VM using this Floating IP from anywhere on the Internet, or connect from other services outside the cloud to your VM!
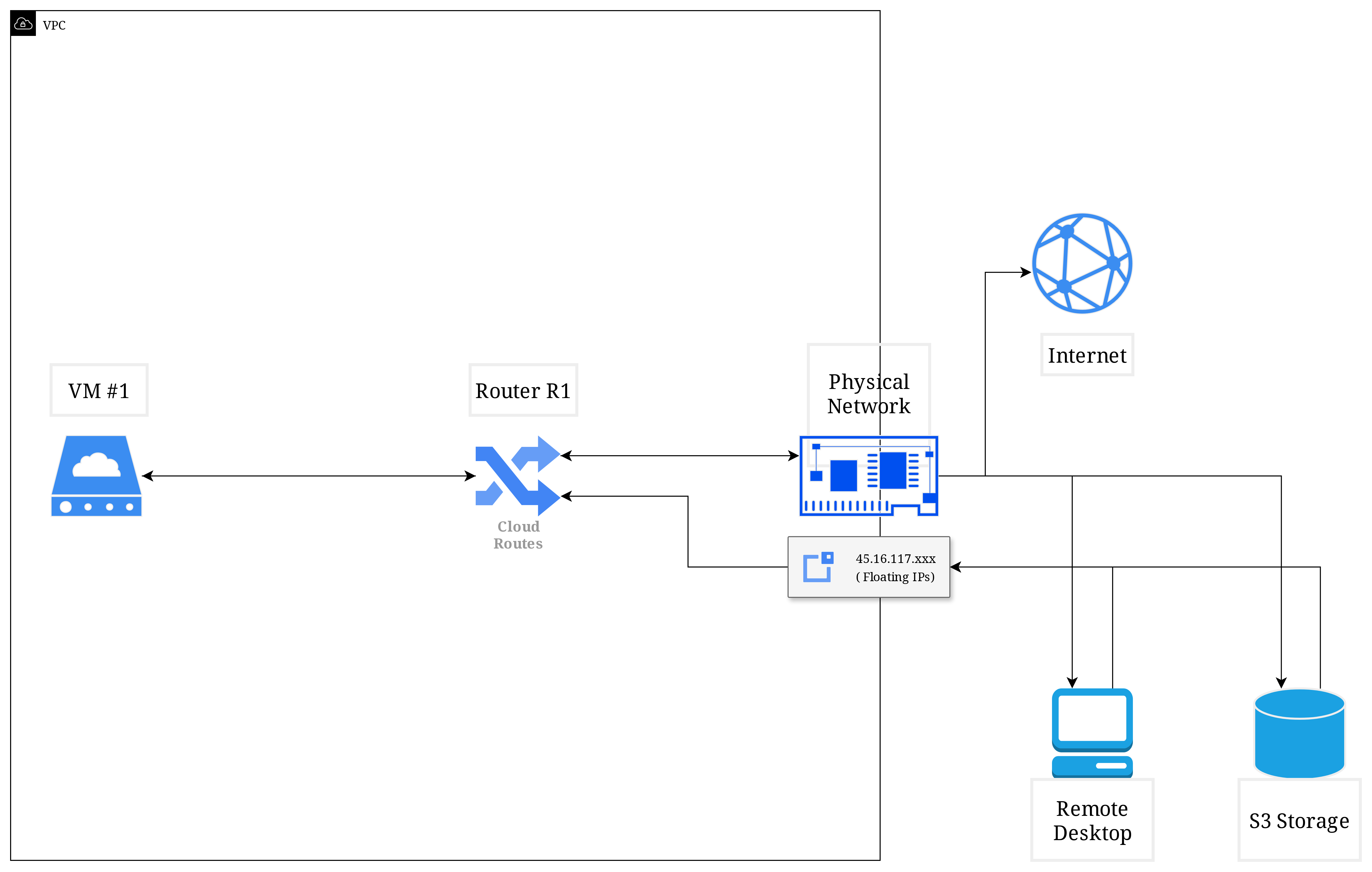
Summary
-
A Router connects your VM's internal network to the Physical Network, allowing it to send and receive traffic from the Internet and other internal networks.
-
A Floating IP is a public IP address that can be dynamically assigned to your VM, allowing you to access it from the Internet.